Connecting external transactional system to a wallet
Introduction
External transactional systems can be connected to a wallet. This way, the system can be notified about the transaction events that happen in the wallet and react to it. In order to achieve that, external transactional system needs to conform to Minka's bridge protocol.
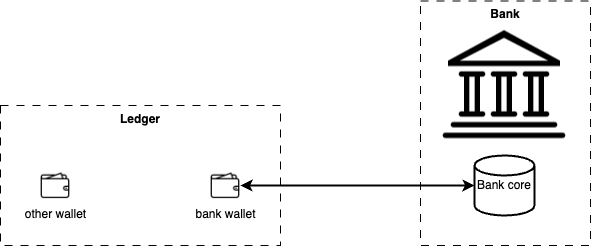
In the image below, the bank core itself implements bridge protocol to establish connection with its dedicated wallet in the ledger.
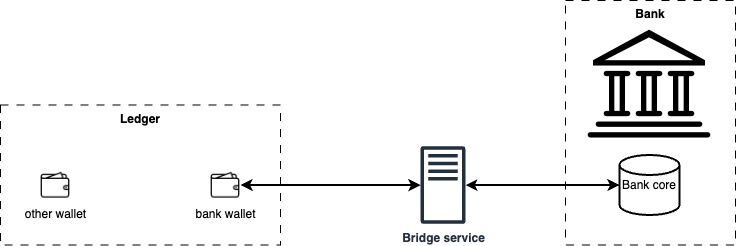
In practice, more common approach is to use a dedicated service - called bridge service - that implements bridge protocol to communicate with the ledger on behalf of the external transactional system. That bridge service acts as a "bridge" between the external transactional system and the ledger. The benefit of this approach is that the external transactional system does not need to implement bridge protocol - instead it is contained in the separate bridge service. This simplifies the integration process. The diagram below shows this approach.
Connecting mint bank to a wallet
For the purpose of this tutorial, we will connect the fictional mint bank to a wallet. To do that, we will need to setup a mocked bridge service and create a dedicated mint-signer signer, and a dedicated mint-wallet wallet in the ledger.
Setting up a mocked bridge service
For the purpose of this tutorial, we will use a mocked bridge service. This service will be used to simulate the communication between the external transactional system and the ledger.
This bridge service needs a dedicated signer to be able to sign the transactions that are made towards the ledger.
Creating mint-signer signer
mint-signer signer will be used to sign the transactions that will be made towards the ledger, on behalf of the mint's bank. It is created using the following command:
minka ledger signer createStarting the mocked bridge service
The bridge service will be started using the following command:
minka bridge startChoose mint-signer signer as the signer for the bridge service.
Also, choose an option to register this bridge service with the ledger and name it mint-bridge. This will create a bridge record in the ledger, which will be used by the wallet to communicate with the bridge service.
Once started, leave the bridge running. It will be used to track the incoming requests from the ledger and respond to them.
Creating a mint-wallet wallet
Download the mint-wallet.json layout file and apply it.
This will create a mint-wallet wallet with the properties the same as previous wallets, but with the bridge field set to mint-bridge. This will allow the wallet to communicate with the bridge service.
Setup overview
Everything is set up and ready to go. The setup looks like this:
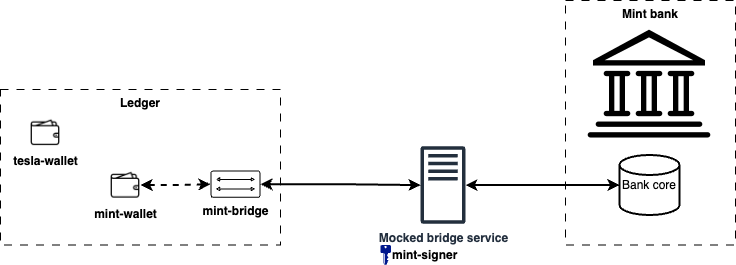
Now, whenever any kind of transaction involving mint-wallet wallet is initiated, the mint-bridge bridge will initiate a request to the mocked bridge service. This will allow external transactional system to react to the transaction events.
Note: For more detailed information about how to build a real bridge service, refer to the Building a bridge service tutorial.